RvtkStatismo: Select from competing points using a statistical model
05 May 2015By request of a user I added the function competingPoints to RvtkStatismo, to select from a set of competing points, those with the lowest Mahalanobis distance calculated from a statistical model (Fig 1).
Here is an example, how to use it:
Create some competing points and test the function
require(RvtkStatismo)
require(Morpho)
require(mesheR)
require(Rvcg)
require(rgl)
mod <- statismoLoadModel(system.file("extdata","mandibles.h5",package="RvtkStatismo"))
mysample <- DrawSample(mod,c(0.215, -0.777, -0.861, -1.871, 1.597, 0.882, -1.225, -0.072, -0.498, 0.094, -0.666, -0.837, -0.145, 0.654))
randomint <- data.frame(sample=sample(1:ncol(mysample$vb),replace=T,size=500))
##get vertices
mysampleverts <- mysamplenoisy <- vert2points(mysample)
## create noisy duplicates of our existing vertices
randomdata <- mysampleverts[randomint$sample,]+rnorm(1500,sd=3)
## now we create the dat to be processed by adding the noisy coorinates as competing ones
competingData <- rbind(mysampleverts,randomdata)
competingIndex <- c(1:ncol(mysample$vb),randomint$sample)
cc <- competingPoints(mod,competingData,competingIndex)
ccmesh <- updateVertices(mysample,cc$goodverts)
wire3d(ccmesh,col="red")
### Hm..., now there are some spikes, because some noisy vertices
### are more probable than the actual ones, when considered isolated.
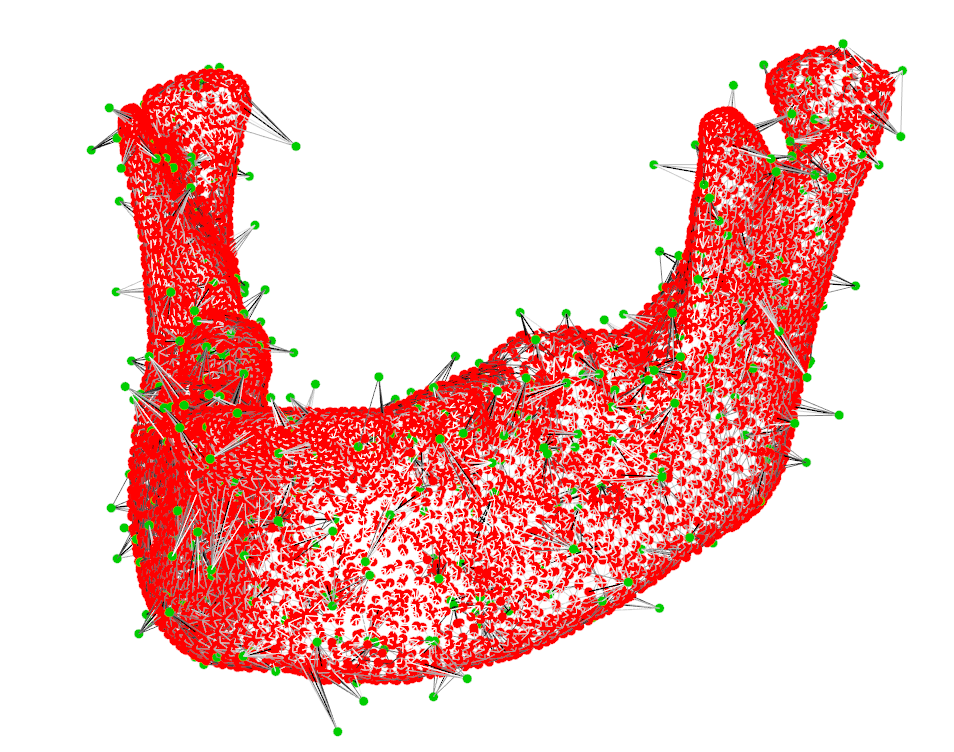
As we can see from Fig 2, some selection seem to have gone wrong, but actually, the “spikes” are exhibiting a lower mahalanobisdistance (when only viewed on an isolated point level):
##get those vertices that do not correspond to the original ones
diffs <- rowSums((cc$goodverts-mysampleverts)^2)
bad <- which(diffs > 0.01)
cc$mahadistance[bad[1]] ##mahalanobis distance of the original vertex
# [1] 5.274545
cc$mahadistance[cc$goodrows[bad[1]]] ##mahalanobisdistance of the selected noisy one
# [1] 1.512667
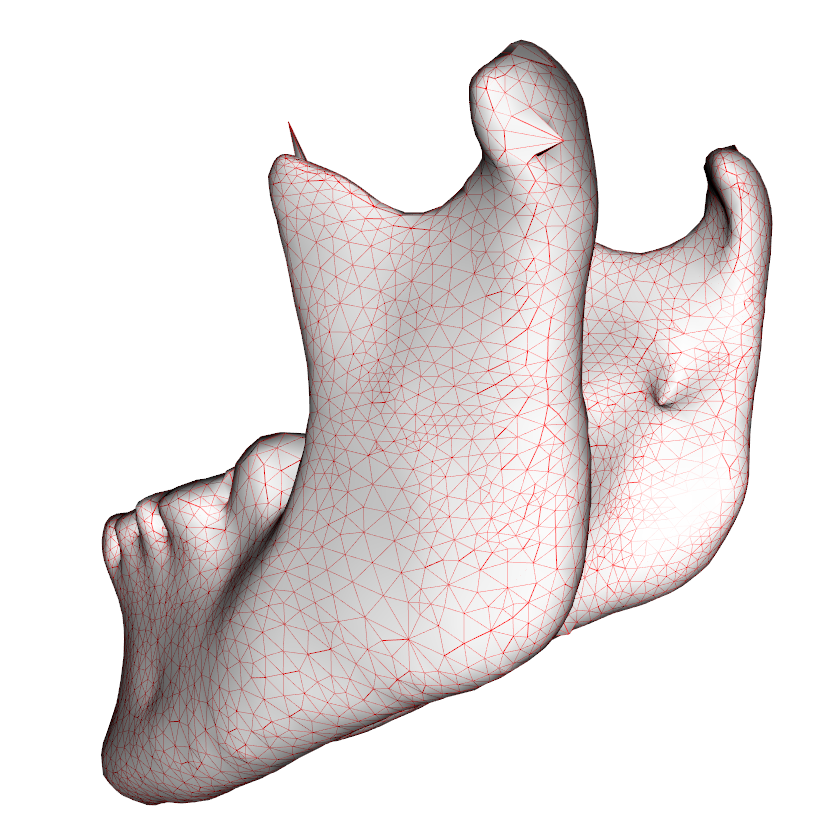
To get rid of those ugly spikes we can either predict the sample from the model or simply smooth it.
## to get rid of those ugly spikes we can either Predict the sample from the model
ccmeshPredict <- PredictSample(mod,ccmesh,align=F)
##or simply smooth it somewhat
ccSmooth <- vcgSmooth(ccmesh)
The final result using the projection into modelspace looks like this (which is identical to its original state):