Update: Displacement fields and smoothing in mesheR
01 Mar 2016While I was at it, I implemented different kernel smoothers and made them also available to the registration function gaussMatch that is based on smooth displacement fields. Additionally, I introduced the function smoothDisplacementField to (surprise, surprise) smooth an existing displacement field.
The smoothing is achieved by calculating weighted averages of neighbouring displacement vectors using kernel functions. These are functions of the distance \(d\) to the respective origin of the displacement vectors. Based on \(d\) and the kernel bandwidth \(\sigma\), the weights \(w(d)\) are calculated as:
Gaussian kernel: \(w(d) = e^{ -\frac{d^2}{2\sigma^2}}\)
Laplacian kernel: \(w(d) = e^{-\frac{d}{\sigma}}\)
Exponential kernel: \(w(d) = e^{ -\frac{d}{2\sigma^2}}\)
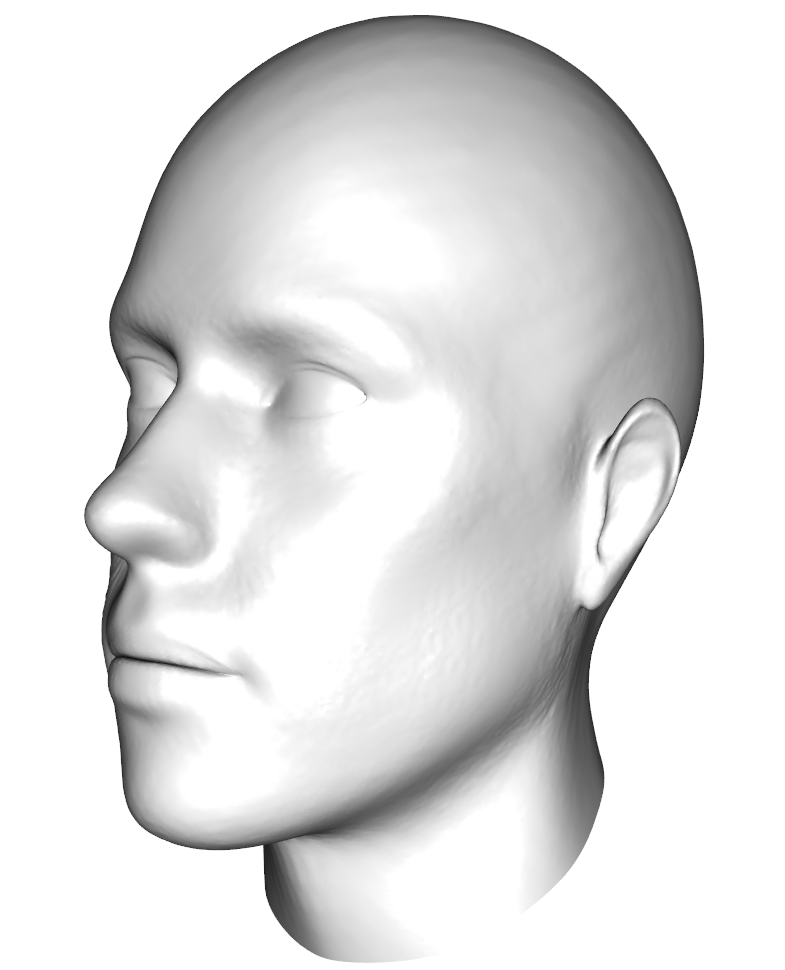
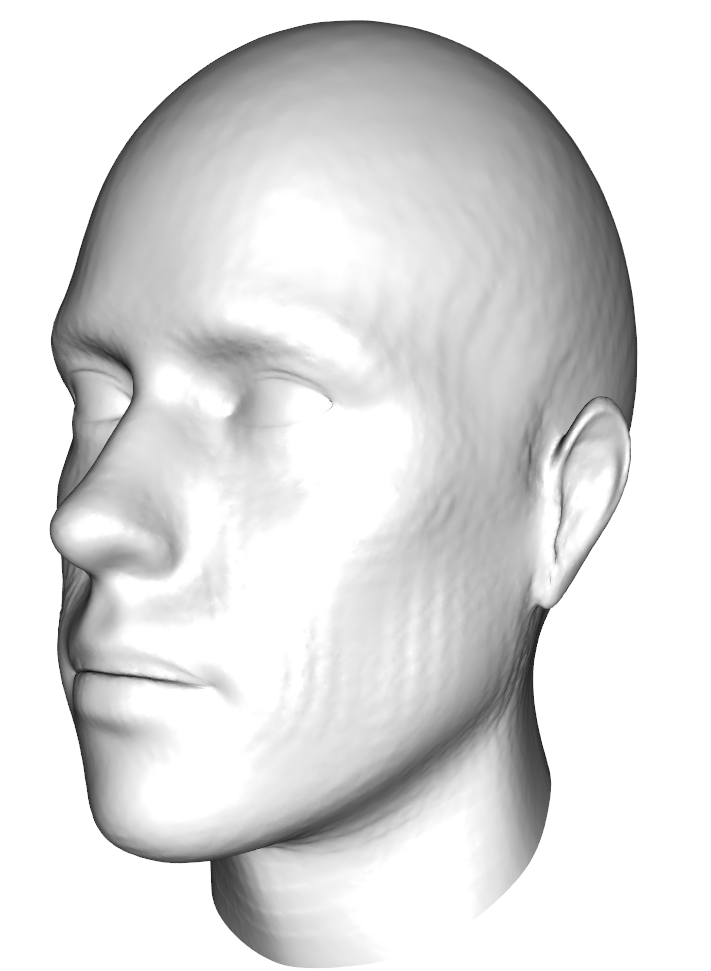
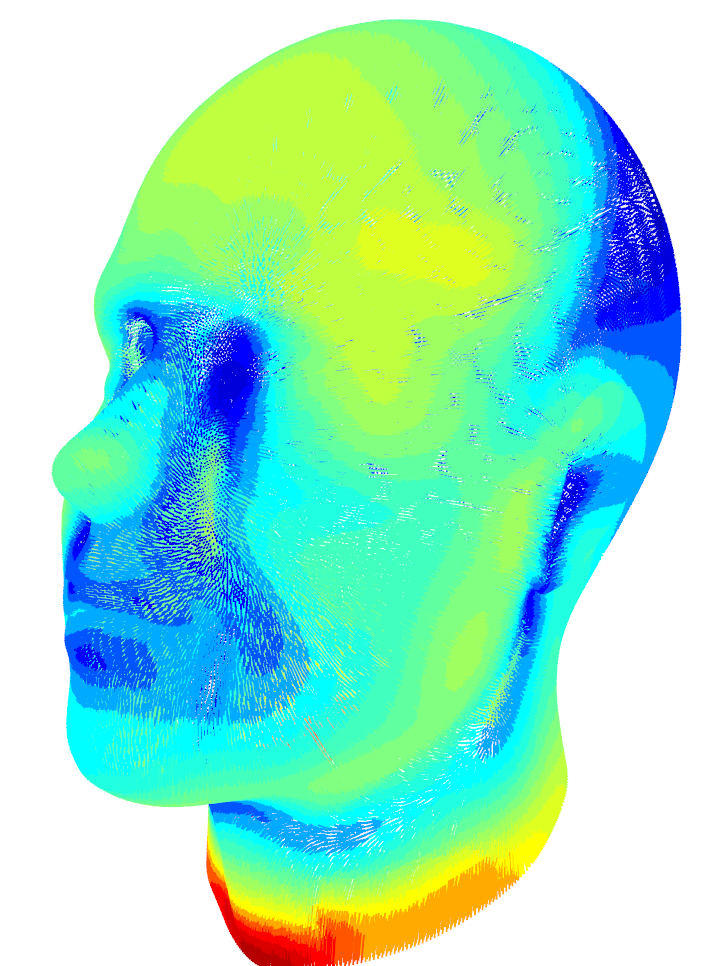
Here an example of the smoothing. First, we register a low resolution mesh elastically to a target and interpolate the displacement field for a finer version of the mesh (Fig. 1). As the result is not yet smooth, we apply additional smoothing to the displacement field (Fig. 2) .
require(mesheR);require(rgl);require(Rvcg)
require(Morpho)
require(Rvcg)
data(humface)
data(dummyhead)
params <- list(iterations=10)
params <- append(params, list(
# first lambda is set relatively high because first matching uses landmarks
# then let it increase from 0.2 to 0.6
lambda=c(0.7,seq(from = 0.2,to=0.6,length.out = params$iterations-1)),
# treat k similar as lambda
k=c(10,seq(from = 1,to=params$iterations-1,by=1)),
useiter=FALSE # iteratively deform dummyhead onto humface
))
#we also want the landmarks to be used in an initial similarity transform
rigid <- list(iterations=30,subsample=200,rhotol=pi/2,uprange=0.6)
similarity <- list(iterations=30, subsample=200,rhotol=pi/2,uprange=0.6)
affine <- list(iterations=30,subsample=200,rhotol=pi/2,uprange=0.6)
map <- AmbergRegister(dummyhead.mesh, humface, lm1=dummyhead.lm,
lm2=humface.lm, iterations=params$iterations,
k=params$k, lambda=params$lambda, useiter=params$useiter,rigid=rigid,
similarity=similarity,affine=affine,forceLM = TRUE)
## rotate/scale the highres mesh to the deformed low-res version
rigidtrans <- computeTransform(map$mesh,dummyhead.mesh,type="s")
dummytrans <- applyTransform(dummyhead.mesh,rigidtrans)
## create the lowres displacement field
dispfield <- createDisplacementField(dummytrans,map$mesh)
## create a smooth highres version of the rotated/scaled reference
highres <- vcgSmooth(vcgSubdivide(dummytrans,type="l",threshold = 1.5))
## interpolate displacement field
highresdispfield <- interpolateDisplacementField(dispfield,highres,k=10,sigma=10,threads = parallel::detectCores())
highres_displaced <- applyDisplacementField(highresdispfield,highres)
shade3d(highres_displaced,col="white") ##Fig. 1
## as the result is not really smooth, we smooth the displacement field
highresdispfield_smooth <- smoothDisplacementField(highresdispfield,k=100,sigma = 100,threads = parallel::detectCores())
highres_displaced_smooth <- applyDisplacementField(highresdispfield_smooth,highres)
shade3d(highres_displaced_smooth,col="white") ##Fig. 2
## finally we plot the smoohted displacement field
plotDisplacementField(highresdispfield_smooth,lwd=2) #Fig.3